Exploring microlearning examples, benefits, and drawbacks
This article provides an in-depth look into microlearning, an adaptable educational strategy that delivers concise, digestible content for efficient and engaging learning experiences. It explores the benefits, drawbacks, practical applications, and popular platforms related to microlearning, providing insights into how it reshapes learning in and outside the classroom.
Introduction
Efficient learning strategies are paramount in a world where technology has become increasingly important. Microlearning is a flexible learning strategy that has gained significant traction recently. This article discusses what microlearning entails, its applications, benefits and disadvantages, and the platforms that support it. We'll discuss how this educational approach makes complex concepts become concise, digestible pieces of content and how it caters to the modern learner's needs. Keep reading this article to learn about microlearning and how to implement it in your classroom.
What is Microlearning?
Microlearning is an educational strategy that refines complex concepts into compact, digestible knowledge. As the term suggests, it presents information in concise, short bursts, each focusing on a specific learning objective. Each unit of study, typically ranging from 3-5 minutes, is standalone and can be reviewed as often as needed, providing flexibility and control to learners. This bite-sized educational approach aligns well with the fast-paced modern lifestyle, offering content that can be conveniently consumed at a time and place suited to the learner's schedule.
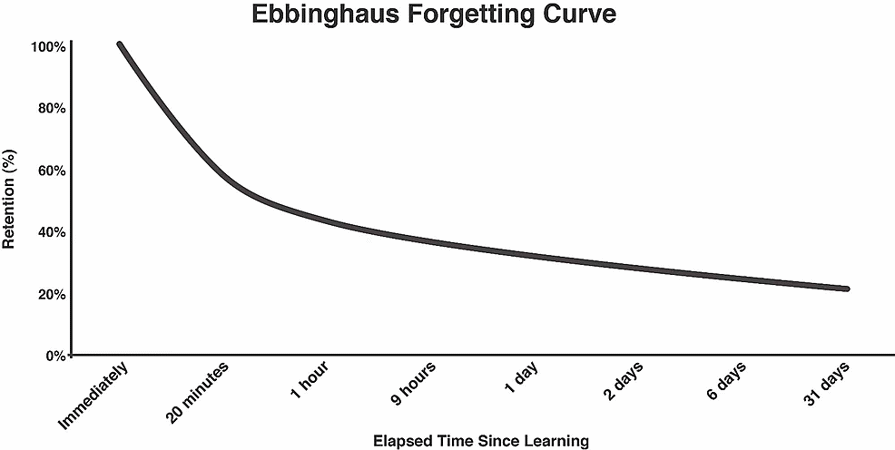
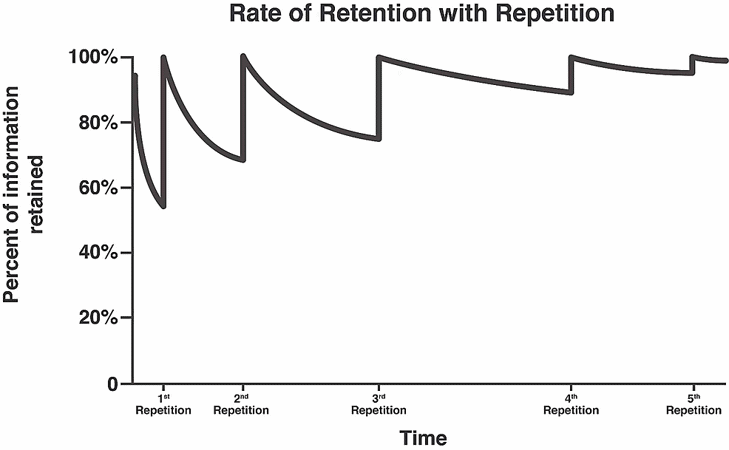
At the core of microlearning's effectiveness is its ability to counteract a psychological phenomenon known as the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve. The curve represents the decline of memory retention over time when there's no attempt to reinforce the learned information. Microlearning's iterative approach can negate this curve, fostering better memory retention. Providing spaced repetition of content and timely reintroductions of learning units ensures knowledge transfer from short-term to long-term memory. Additionally, breaking complex lessons into smaller, manageable units helps to avoid mental fatigue, thus improving attention, motivation, and memory retention, as suggested by Shail (2019).
One of the distinguishing features of microlearning is its adaptivity. Rather than subjecting all learners to the same content, it individually tailors content and activities based on each learner's mastery goals and past performance. This personalization allows for a focused learning experience, significantly improving engagement and outcomes.
Scientific evidence bolsters the effectiveness of microlearning, suggesting that it improves retention and speeds up the learning process. Shail (2019) explains that the compact nature of microlessons helps learners avoid cognitive decline due to mental fatigue and keeps engagement levels high, mainly when delivered through varied forms of media on mobile devices. A study by Nikou (2018) also highlighted this finding, with a proposed mobile-based microlearning approach improving student learning performance and motivation in secondary school science education. Microlearning enables learners to keep track of their progress and to adjust their learning pace if required, making these advantages more apparent.
An engaging factor of microlearning lies in its concise format. A brief text, a quick video, or even a short quiz does not require significant time or attention commitment, making it appealing to the modern learner. It is analogous to why social media platforms like Twitter and TikTok thrive—their bite-sized content suits the consumer pattern of today's generation. Thus, microlearning aligns with current needs, delivering effective learning in an appealing, easily consumable manner.
Examples of Microlearning
Microlearning has proven its versatility not only in corporate settings but also in K-12 education. Microlearning applications extend beyond the workplace, reaching foundational education and ensuring students grasp essential concepts effectively and efficiently. Let's explore a few practical examples of how educators can implement microlearning in the K-12 system.
Math Facts Practice
Math facts practice is a primary use case. Fundamental math facts, such as addition and multiplication tables, form the base for advanced concepts. Memorizing these can be a mundane task. However, educators can utilize online tools such as Math Playground or Khan Academy to offer students short, interactive math games targeting specific math facts.
Students can complete these activities in a few minutes: they are an excellent way to integrate learning into their daily routines. However, educators must remember that implementing microlearning and similar tools requires careful planning. Teachers can use i3LEARNHUB to prepare microlearning modules, easing the digital transformation of the classroom and ensuring that students have access to them at their convenience. Google Classroom is an additional tool that can aid in the complete follow-up of student progress.
Vocabulary Building
Shifting gears from math to language learning, another significant application of microlearning lies in vocabulary building. A robust vocabulary is a pillar for academic success; traditional teaching methods can be tedious and ineffective. Tools like BookWidgets or Quizlet can make this process engaging by creating brief quizzes or flashcards focusing on specific words or concepts. They can be completed quickly, encouraging students to review vocabulary regularly. Integrating these tools into an i3LEARNHUB learning path makes it even easier, with BookWidgets grades being automatically sent to the teachers' learning system's grade book.
Writing Prompts
Teachers can also use microlearning when preparing writing prompts. Writing is an essential skill for academic and professional success. To assist students in overcoming obstacles like writer's block, teachers can provide short writing prompts focusing on specific topics or genres. AI tools like Bing or ChatGPT can help initiate the process and simultaneously stimulate discussions about the appropriate and ethical use of these tools.
Science Experiments
In the realm of science, experiments are another great microlearning example. While they are a great way to understand scientific concepts, traditional experiments can be time-consuming and messy. Teachers can use tools like Mystery Science to give students short, interactive experiments focusing on specific concepts. Students can also conduct more advanced digital scientific experiments via PhET. These interactive simulations, integrated into i3LEARNHUB, provide a convenient platform for teachers to create personalized microlearning experiences.

Language Learning
Language learning presents another application for microlearning. Learning a new language can be overwhelming. However, breaking it down into smaller, digestible parts using tools like Duolingo makes it more manageable. Students can quickly complete short, interactive language lessons focusing on specific vocabulary or grammar concepts, making language learning a part of their daily routine.
These examples of microlearning showcase the diversity of possible learning formats with this pedagogical strategy. Microlearning can range from reading a short article, watching a tutorial video, and participating in a brief interactive learning module to using digital flashcards or answering an online quiz. This concise yet effective learning method employs interactive learning technologies to make education more engaging and for many other benefits. In the corporate world, micro-training sessions allow employees to balance their regular work while continually enhancing their skills. Similarly, in a school setting, students can use microlearning to supplement their traditional learning in a more engaging manner, all while fitting conveniently into their daily routines. Let's now explore the benefits of microlearning in education.
Benefits of Microlearning
Microlearning is an impactful educational strategy ideal for today's fast-paced society. It presents concise, manageable content pieces like short texts, videos, and podcasts, accommodating the modern learner's lifestyle.
Benefits of microlearning include, among others:
- Flexibility. Microlearning requires minimal time and attention, fitting conveniently into busy schedules and catering to shorter attention spans.
- Adaptability. Microlearning permits integrating diverse multimedia elements, increasing engagement levels such as audio, video, or images.
- Immediate gratification. Microlearning is particularly effective in onboarding and training scenarios, where users can quickly acquire and apply knowledge.
- Personalization and ease of consumption. Microlearning tackles one topic per module, reducing cognitive load and aiding retention. Studies confirm a significant boost in retention rates (Shail, 2019)
- Learning efficiency. Deconstructing complex subjects into smaller units fosters efficient content development and learning transfer, making it a cost-efficient learning solution.
Disadvantages of Microlearning
Despite the many advantages of microlearning, it is essential to acknowledge its limitations. While many praise this teaching strategy for its brevity and flexibility, these attributes can become drawbacks in specific learning contexts.
The first significant disadvantage of microlearning is limited depth. The bite-sized approach, which is excellent for providing quick and digestible information, may fall short when covering complex subjects requiring extensive exploration and explanation. This abbreviated teaching method might not give the learners enough detail to understand complex topics or to appreciate the larger context within which a specific piece of information fits.
Linked to this is the issue of a lack of context. Pursuing brevity, microlearning modules sometimes fail to explain how a particular piece of knowledge fits into a larger framework, making it challenging for learners to understand the subject matter comprehensively.
Another drawback is the absence of a traditional learning environment, which could affect the commitment and focus of learners. While microlearning's resemblance to a social media environment can foster behavioral and emotional engagement and enhance intrinsic motivation, it may also contribute to a less formal atmosphere that can potentially undermine serious learning efforts. According to Fidan (2023), microlearning might not offer the ideal learning conditions for learners who thrive in structured, traditional educational settings.
Furthermore, disparities in technology access can create a significant barrier to the successful implementation of microlearning. This teaching method relies heavily on digital platforms, so learners without consistent and reliable access to technology, especially in regions with low connectivity, might be disadvantaged.
Lastly, despite the potential personalization benefits of microlearning, the learning experience may not always be optimally tailored to learners' needs and capabilities, potentially limiting retention and understanding.
While one can acknowledge that microlearning offers many advantages, it's essential to understand its potential drawbacks when designing a comprehensive and effective learning strategy. Ultimately, the optimal approach might be a balanced blend of microlearning with other teaching methods tailored to learners' needs and context.
Popular Microlearning Platforms and Apps

Many dedicated platforms and apps are available for students interested in microlearning. These digital tools enable bite-sized, customized learning experiences that align with individual learners' needs and preferences.
Established online learning platforms such as Coursera, Udemy, and Khan Academy have significantly facilitated the microlearning approach. They offer micro-courses catering to numerous academic disciplines, including languages, science, humanities, and mathematics. The mobile-optimized design of these platforms gives learners the convenience of accessing educational content anytime, anywhere, reinforcing the flexibility that microlearning embodies.
In addition to these platforms, several microlearning applications focus specifically on promoting this compact, focused learning approach in an educational context. For instance, Qstream uses scenario-based quizzes to encourage active learning and improve knowledge retention, a valuable tool for students who need to understand and apply complex concepts.
7Taps, with its minimalist design, provides lessons in an easy-to-digest format, perfect for students trying to grasp new concepts quickly. Its three-minute lesson format also aligns well with the decreasing attention spans of today's learners.
Learnie presents an innovative learning paradigm by encouraging users to create, share, and collaborate on microlearning paths. This promotes a community-based learning environment, useful in group projects and collaborative academic tasks.
GoSkills focuses on providing learners with personalized, bite-sized courses. This platform can be a helpful resource for students interested in acquiring specific business skills or exploring entrepreneurial concepts.
i3LEARNHUB supports using interactive whiteboards for collaborative and active learning in classrooms and virtual environments, improving learning outcomes. It provides a platform for creating and sharing short, interactive lessons, making it a valuable tool for implementing a micro-learning approach in a traditional or virtual classroom setting.
Edgagement employs multimedia to provide engaging learning content, ideal for visual learners and students who thrive on interactive educational content. EdApp, similarly, integrates gamification and spaced repetition into its courses to enhance engagement and retention, strategies that can make learning more exciting and compelling for students.
These various microlearning platforms and apps, each with its unique approach and features, offer diverse and flexible solutions for learners. Whether for academic enrichment, specific subject learning, or collaborative educational tasks, microlearning tools provide a range of possibilities that can revolutionize how students learn.
Conclusion
Microlearning has emerged as an effective educational strategy for reshaping our learning and teaching. Its focus on delivering concise, bite-sized content provides an efficient, engaging, and personalized learning experience that aligns well with the contemporary learner's needs. From K-12 education to corporate training, microlearning has many potential applications. Teachers must remember that microlearning may not be the best strategy for every learning scenario, but it can substantially enhance learning outcomes when appropriately implemented.
Frequently Asked Questions About Microlearning
What is microlearning?
Microlearning is an educational strategy that refines complex concepts into compact, digestible knowledge. It presents information in concise, short bursts, each focusing on a specific learning objective.
How can microlearning be applied in a K-12 setting?
Microlearning applications extend beyond the workplace, reaching foundational education and ensuring students grasp essential concepts effectively and efficiently. Examples of microlearning in K-12 education include practicing math facts with online interactive games, vocabulary building with brief quizzes or flashcards, short writing prompts, interactive science experiments, and digestible language lessons.
What are the benefits of microlearning?
The benefits of microlearning include:
- Flexibility
- Adaptability
- Immediate gratification
- Personalization and ease of consumption
- Learning efficiency
It fits conveniently into busy schedules, integrates diverse multimedia elements, allows quick knowledge acquisition, reduces cognitive load, and fosters efficient content development.
What are some drawbacks of microlearning?
Despite its many advantages, microlearning also has its limitations. It may lack depth when covering complex subjects requiring extensive exploration. Context may sometimes be lost in the pursuit of brevity. Its resemblance to a social media environment might undermine serious learning efforts for some learners. Disparities in technology access can also create barriers to its successful implementation.
What platforms or apps support microlearning?
Many platforms and apps, such as Coursera, Udemy, and Khan Academy, support microlearning. These platforms offer micro-courses in numerous academic disciplines. Additionally, apps like Qstream, 7Taps, Learnie, GoSkills, i3LEARNHUB, and Edgagement promote the compact, focused learning approach in an educational context.
References
Fidan, M. (2023). The effects of microlearning-supported flipped classroom on pre-service teachers' learning performance, motivation and engagement. Education and Information Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11639-2
Forgetting curve. (2023). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Forgetting_curve&oldid=1142477494
Nikou, S. A., & Economides, A. A. (2018). Mobile-Based Micro-Learning and Assessment: Impact on learning performance and motivation of high school students. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 34(3), 269–278. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12240
Shail, M. S. (2019). Using micro-learning on mobile applications to increase knowledge retention and work performance: A review of literature. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.5307

